Educational Digital Twins: The Virtual Lab Empowering Tomorrow’s Engineers
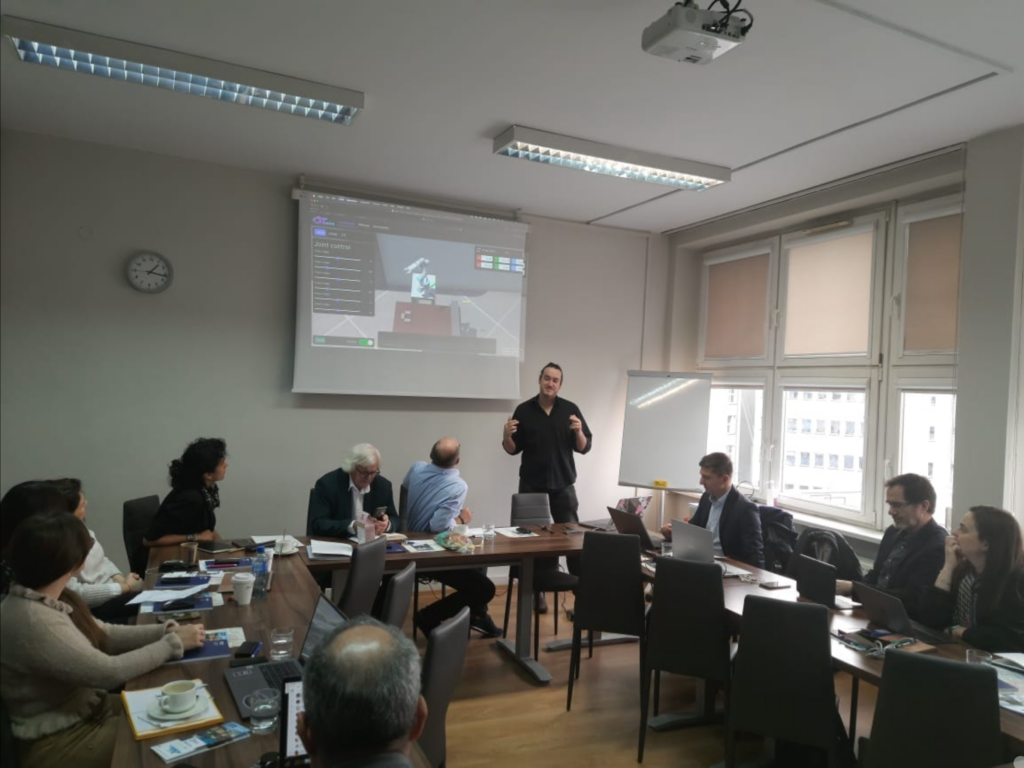
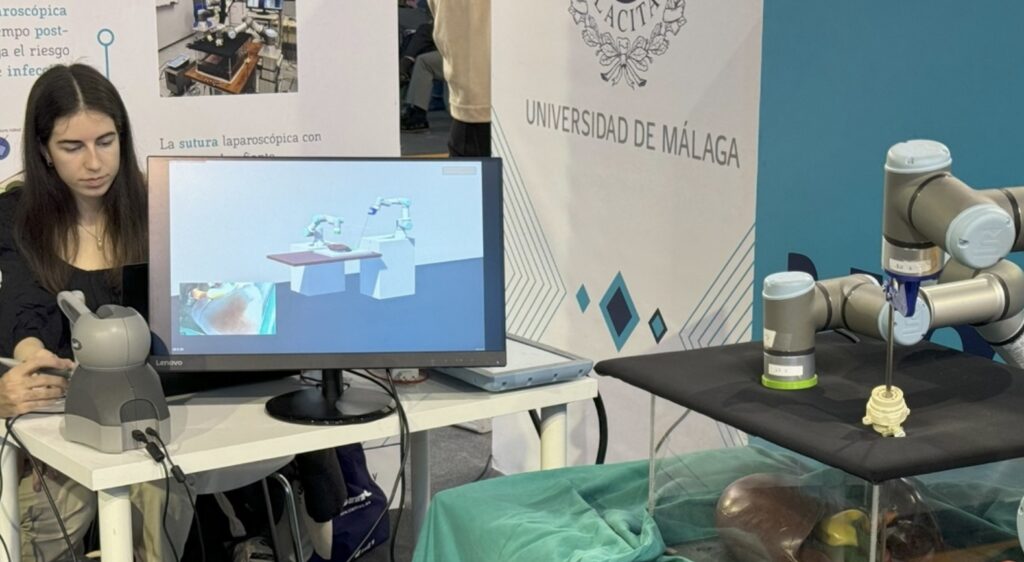
Imagine a boundless laboratory where future engineers design, test, and refine complex processes with a single click. Educational digital twins bring this concept into the classroom: virtual replicas that combine simulation, virtual reality, and remote connection to real equipment. A student can mix chemicals in a virtual chemistry lab, route traces on a circuit board, or program a robotic arm—all in a safe environment with no time or cost constraints. With a pair of VR classes, the experience becomes fully immersive, and from anywhere, the student can send their code to a physical robot to verify its real-world performance. This approach not only reduces risks and expenses but also fosters creativity and confidence, preparing the next generation for the hyperconnected industry of the future. The Simulation-Based Digital Twin as a Teaching support With an educational digital twin, students dive into a virtual environment where simulation allows them to interact with and modify real processes without limits or danger. In a chemistry lab, for instance, simulation lets them drag and drop reagents, adjust proportions, and watch the reaction evolve in real time, repeating experiments as often as desired at no extra cost. In engineering, circuit board design simulation enables students to trace connections, select components, and run thermal and electrical stress tests on the virtual model—all with a single click, instantly spotting faulty solder joints or potential short circuits before moving to physical production. Immersive Digital Twins An additional step in the evolution of educational digital twins is the integration of an immersive environment that enhances the feeling of being beside real equipment. Through high-fidelity 3D representations and virtual reality glasses, students can “walk” around the machine, inspect its parts, and interact as if in a physical lab. For example, when programming a robotic cell, the student can design the arm’s motion sequence, view it from the operator’s perspective, and verify in real time whether the path is safe and efficient. Similarly, simulating a production line allows students to navigate each station virtually, ensure tools are properly calibrated, and correct any part misalignment or collision. This immersive approach not only aids spatial understanding and decision-making but also builds confidence: if the program fails, they see it immediately; if it succeeds, they can view it from every angle before applying it in the real world. Thus, combining simulation and VR transforms learning into a safe, engaging experience, bridging the gap between theory and practice. Cyber-Physical Systems: The Remote Lab for Teaching The final stage in teaching with educational digital twins is the remote lab, where the virtual model connects directly to the physical system to operate together. Returning to the robotic cell example: after designing and validating the motion sequence in simulation, the student can send their program to the real robot in the lab—even if they are on the other side of campus or in a different city. This setup unlocks access to high-cost equipment that most teaching centers would otherwise lack. Students get a “real lab” experience without needing to be physically present, learn to handle latency and safety aspects of remote control, and verify in real time whether their code runs correctly in the real world. Moreover, the remote lab offers greater scheduling flexibility and optimizes resource usage: multiple students can take turns testing their solutions while the robot automatically executes each programmed task. Conclusions By integrating real-time simulation, immersive virtual environments, and remote-access capabilities, educational digital twins break down geographical and financial barriers to high-end equipment. This democratization of technology empowers students everywhere to gain hands-on experience with cutting-edge systems—from robotic cells and automated production lines to complex laboratory setups—without the constraints of physical presence or prohibitive costs. As they design, test, and refine virtual replicas before deploying code and configurations on real hardware, learners develop critical skills in system modeling, troubleshooting, and safety protocols. Ultimately, this holistic approach cultivates a generation of engineers who are not only technically proficient but also adept at working in distributed, cyber-physical contexts—precisely the competencies required to drive innovation in today’s hyperconnected industries.
Educational Digital Twins: The Virtual Lab Empowering Tomorrow’s Engineers Read More »